You can maintain your Organization plan in Organization Management using a number of different interfaces.
Organization Management: Includes various user group-specific modes and views with which to edit organizational plans.
Organization & Staffing: Provides an intuitive interface for creating and editing an organizational plan.
General Structure: Allows you to edit organizational plans with any structures including object types that you have defined yourself.
Matrix View: For creating and editing matrix structure.
Infotype Maintenance: Allows you to edit the characteristics of various objects and their relationships via info types.
Simple Maintenance: Provides an overview of object and structure editing.
Structural Graphics: This enable you to view objects and structures, and person a variety of maintenance activities for the objects in graphical format.
| Want to acquire industry skills and gain complete knowledge of SAP BASIS? Enrol in Instructor-Led live SAP BASIS Training to get Job Ready! |

You can maintain any number of plan versions. Plan versions allow you to create several organizational plans in the system at the same time. You can simulate and compare various scenarios using plan versions.
One of these plan versions represents the active organizational plan and is flagged as the active integration plan version. [PL0G PLOG1]
Object Types: There are 5 Basic object types; each has its own object type key.

Org Unit (O):
Organizational units describe the various units in your enterprises that are usually structured according to tasks and functions.
E.g.: Company Departments.
Jobs are general classifications for sets of tasks or functions that an employee is required to perform.
Positions are specifications tied to the organizational units and are held by the individual in the enterprise.
E.g.: Sales Managers, HR managers
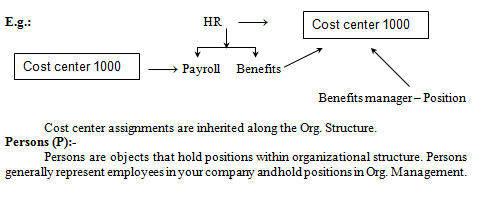
Cost Centers (K):
Cost centers can be related to Org. Units and Positions.
Tasks describe the responsibilities of jobs & Positions
E.g.: Job – Manager – Tasks – managers department – Coordinates meetings
Work centres describe the physical locations where tasks are performed.
E.g.: Corporate office plant.
Other Object types:
Budget – BU – Designed to Org. Unit
Qualification – Q – Assigned to Persons, Jobs, and Positions.
Object Relationships:
| Checkout our Blog on SAP HR Tutorial |

A relationship may also be one-sided. Relationships to objects of an external object type (cost center in controlling for example ) are one-sided, that is, they only go in one direction.




The relationships between the basic object types give rise to structures.
Eg: Org. Unit
Positions
Employee
Once you have created the structure along with objects and relationships. You can assign additional characteristics to the objects.
Object characteristics are maintained in info types
Object Org unit, Position, Job
Relationship Belongs to, reports to
Description of General Text
Cost Planning Cost elements
Address First Address, Second Address
When an object is created, an object ID must be assigned

Validity dates:
Allows you to evaluate the organizational structure on key dates.
Class 1: Information must exist for the entire life cycle of the object but can be changed.
E.g.: An object must have a short name. This information must exist uninterrupted but can be changed.
Class 2: Information is optional but can exist only once within a user-defined period.
E.g.: A position may only have one vacancy info type at a time.
Class 3: Information is optional and the number of data records that can exist within a user-defined period.
E.g.: Sales department can be related with the number of positions simultaneously.
Class 3 with Additional Conditions: Information is optional, and the number of data records that can exist within a user-defined period is dependent on the type of target object.
E.g.: A position can be described by only one Job but by a number of tasks.
Navigation Overview:
Menu: Settings & Commands |
|
| Search Area: Finding Area | Overview Area: Displaying / Maintaining Object environment |
| Selection Area: Selecting Objects | Detail Area: Displaying / Maintaining Object Characteristics. |
Infotype is accessed directly from object maintenance. Objects with various statuses can be maintained.
T Code: PP01.
HR → OM → Expert Mode
Infotypes:
Object: Validity period, status, object Abbreviation, Name
Relationships: Relationship info type allows you to define the relationships that exist between different objects.
Infotype Maintenance – Manually Create a Relationship.
Simple Maintenance-System automatically creates relationships
Structural Graphics-System automatically creates relationships
Description: Allows you to append long text description
Vacancy: Allows you to identify position vacancies. A vacancy occurs when a position is not occupied either currently or at some point in the future but is to be occupied again.
Positions cannot be flagged simultaneously as vacant and obsolete if a vacant position is flagged is obsolete, the vacancy is delimited at the start of the validity of the obsolete flag [minus one day].
If you want to activate integration with recruitment you need to maintain vacancies using this info type.
Obsolete: This info type denotes positions that are no longs necessary but are still occupied. As soon as the position holder leaves the position a dialog box answers asking is you would like to admit.
| Read these latest SAP HR Interview Questions and Answers that help you grab high-paying jobs! |
For O.M. users, simple maintenance is best used to establish the basic framework in organizational plan development.
Simple Maintenance uses a free structure, which allows you to create a basic framework for organizational plans, using streamlined procedures.
Initial screens:
There are three main areas in simple Maintenance depending on whether you want to edit organizational structures, staff assignments or track profiles.
Change Organizational structure:
This screen allows you to build up and maintain the organizational structure for your organizational plan
Change Staff Assignments:
This screen allows you to identify the staff assignment required for an organizational plan.
Change Task profile:
This screen allows you to create maintain and view task profile for Org. units, jobs and positions.
Views:
You can work with simple Maintenance using one or two
Views: (i) Overall view
(ii) Human Resources View
(i) Overall View:
You can work with: tasks, standard tasks, workflow tasks, workflow templates, and roles.
(ii) Human resources view:
You can only work with tasks and standard tasks.
Reporting Structure:
Refers to relationships between positions. Positions may be subordinate to other positions.
You can display a complete reporting structure using report ‘RHSTRU00’
INTEGRATION:
Organizational Assignment
If integration is active the fields Org. Unit, Job, and Cost centre in the Assignment is field from Organization management and accept no input.
Integration settings:
Group Sem. --- Value --- Description
PLOG1 ORGA X - Integration Switch: Org. Mgmt
PLOG1 PRELI 99999999 - Integration: Default Position
PLOG1 TEXTC X - Integration: Transfer short text of job
PLOG1 TEXTO X - Integration: Transfers short text of
Org. Unit
PLOG1 TEXTS - Integration: Transfer short text of
Position
PLOG1 EVENB X - Enhanced Integration (X = On,
Space= Off)
PLOG1 EVCCC 02 - Master Data action: Company code
Change
PLOG1 QUALIA 032 Q - Integration Qualification / Personal
Data
q If you activate the PLOG1 ORGA switch you enable the following: Transfer to Personnel Admin of changes to object relevant for integration. [E.g.: Org. units, Positions, Jobs]
q You must also set the integration plan version in the entry PLOG1 PLOG1. If you do not an integration plan version, integration is not active.
The following reports are relevant for the transfer of data from Org. management to Personnel Administration.
q RHINTE00
q RHINTE10
q RHINTE20
q RHINTE30
RHINTE 00: If you have already HR Master Data, You must start the report ‘RHINTE00’.
RHINTE 10: generate the required table enters in Personnel Admin for Org. Management Objects that are relevant for integration.
RHINTE 20: Checks whether all of the objects relevant for integration exist in both personnel Administration and Org. Management.
RHINTE 30: Transfer a person's Organization agreement (Positions, Org units) from Org. management to the Org. Assignment (IT0001) info type of Personnel Administration.
Some Important Infotypes used:
Infotype Infotype Text
1000 Object
1001 Relationships
1002 Description
1003 Department/Staff
1004 Character
1006 Restrictions
1007 Vacancy
1008 Account Assignment
1009 Health Examinations
1010 Authorities and Resources
1011 Work Schedule
1013 Employee Group/Subgroup
1014 Obsolete
1015 Cost Planning
1016 Standard Profiles
1017 PD Profiles
1018 Cost Distribution
1019 Quota Planning
1027 Site Dependent Info
1028 Address Infotype
1032 Mail Address
1039 Shift Group Infotype
1208 SAP Organizational Object
1222 General Attributes Maintenance
You liked the article?
Like: 0
Vote for difficulty
Current difficulty (Avg): Medium

TekSlate is the best online training provider in delivering world-class IT skills to individuals and corporates from all parts of the globe. We are proven experts in accumulating every need of an IT skills upgrade aspirant and have delivered excellent services. We aim to bring you all the essentials to learn and master new technologies in the market with our articles, blogs, and videos. Build your career success with us, enhancing most in-demand skills in the market.